Mathematics
The Scienteens Lab offers five different mathematics workshops for secondary school classes. They focus on topics such as graph theory, probabilities, cryptography, classification and modelling. Most of these workshops are designated for students aged 16 to 19. They take place on Campus Belval, under the supervision of the Scienteens Lab’s team. Each workshop is described in the table below. You can also get a glimpse of our mathematics workshops through a short video.
This workshop gives the pupils an introduction into the theory of probability and its basic mathematical notions and concepts. Practical exercises that the pupils carry out by themselves help them to gain a clearer understanding of how to deal with probabilities. By means of specific examples, for instance from the field of medical sciences, they also see how concepts from probability theory can help to make decisions.
The workshop covers among others the following concepts
- Basic notions (random variable, expected value, distribution)
- Bernoulli experiment and the binomial distribution
- Geometric distribution
- Conditional probability
- Examples and applications of probability theory
This workshop is suited for pupils from 3e onwards.
The workshop is flexible and the pace is adapted to the level of each class.
During this workshop, the pupils get an introduction to graph theory and learn how different theoretical concepts are used to model and solve problems that arise in daily life, for example in logistics and planning. The pupils can actively participate in the workshop and in various practical exercises, they have the opportunity to test by themselves the concepts addressed by the workshop.
The workshop covers among others:
- the problem of the seven bridges of Königsberg
- Eulerian and semi-Eulerian graphs
- weighted graphs
- Dijkstra’s algorithm to find the shortest path
- the Traveling Salesman problem
- Google’s PageRank algorithm
- applications of graph theory in daily life
This workshop is suited for pupils from 4e onwards.
This mathematics workshop allow students to learn how number theory is applied to secure communications. Through practical exercises such as decryption of a coded message with a cipher wheel, the student will discover how an encryption algorithm works and understand the underlying number theory.
They will tackle different mathematical concepts:
- the Euclidean division (division with remainder)
- the greatest common divisor
- the extended Euclidean algorithm
- Fermat’s little theorem
- the RSA-algorithm
If the teachers wish to prepare their classes before the workshop, corresponding materials that can be used to work with the students will be provided. (For more details see the Prerequisite tab)
This workshop is suited for pupils from 3e onwards.
The workshop is flexible and the pace is adapted to the level of each class.
The concept of classifying objects – grouping them into different categories – according to certain criteria, plays an important role in many sciences. In biology for example, organisms are classified based on common characteristics and evolutionary relationships. In mathematics, exactly the same happens and many mathematicians are concerned about the classification of mathematical objects.
This workshop introduces the concept of classification and illustrates its importance in science and mathematics. Through examples such as numbers, graphs or geometric shapes, the pupils see how mathematical objects can be classified and further learn how so-called invariant properties can be used to distinguish objects.
This workshop is suited for pupils from 3e onwards.
This workshop gives students an overview of mathematical modelling and shows them how real-world problems can be modelled and solved using mathematics. It is divided into two parts.
During the first part, students learn how to formulate a linear optimisation problem and how a problem with two variables can be solved graphically. They then learn about the simplex algorithm that can be used when there is more than two variables.
The second part is dedicated to modelling growth processes and deals in particular with the SIR model, which is used to model the spread of an epidemic in a given population.
The workshop covers, among other things:
- Examples of linear optimisation problems
- Graphical resolution of a two-variable problem (using GeoGebra)
- The simplex algorithm
- Linear, exponential and logistic growth
- The SIR model and its implementation in GeoGebra
This workshop is suited for students from 3e onwards.
It can be offered either as a full-day (6.5 hrs.) or as a half-day (3-4 hrs.) course.
For the half-day version of the workshop, the class must choose between the two parts (i.e. optimisation or population dynamics).
For the part on the simplex algorithm, it is useful if students already have some knowledge in manipulating systems of linear equations.


Practical information for all mathematics workshops
All the mathematics workshops are suitable for classes ranging from 3rd to 1st grade (in the Luxembourgish school system), meaning students aged 16 to 19.
Workshop 2 (graph theory) is also suitable for classes from the 4th grade.
The workshops can be given in Luxembourgish, French, German or English.
Workshops 1, 2 and 5 (probability, graph theory and modelling) can be offered either as a full-day (6.5 hrs.) or as a half-day (3-4 hrs.) course. Workshop 3 (number theory) can only be offered as a full-day course. Workshop 4 (classification) can only be offered as a half-day course.
The full-day workshops take place from 9:00h till 15:30h with a lunch break of one hour. During the lunch break the students can get some food from the restaurants that are located on Campus Belval and in Belval Plaza, or they can use the canteen. The lunch schedule need to be observed, so that the afternoon activities can resume on time.
Teachers who choose the half-day version of the course are free to choose their preferred starting time (can be done during registration procedure).
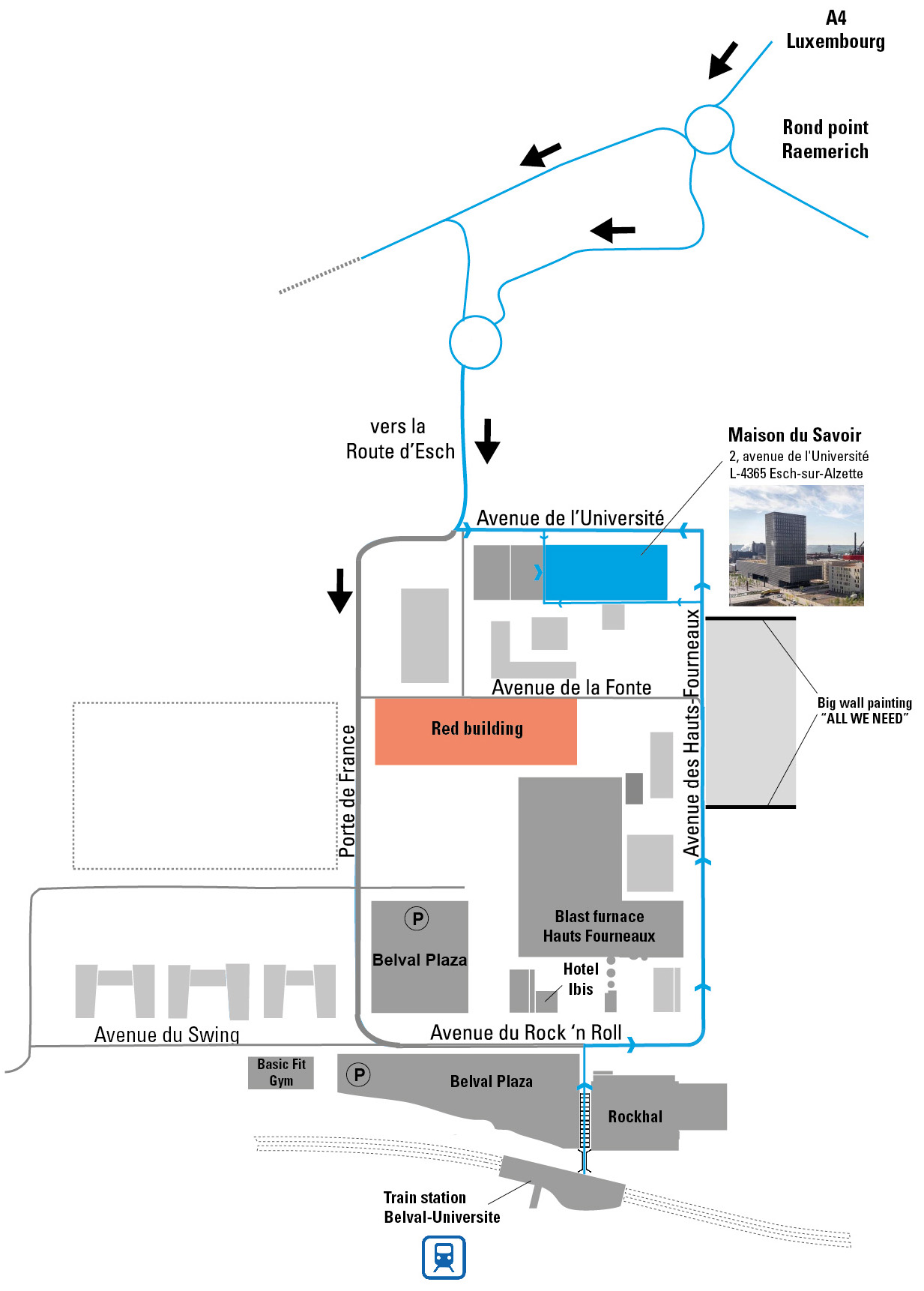
The workshops in mathematics take place in the Maison du Savoir (MSA) on Campus Belval.
If you arrive by car or coach, take the A4 and keep it until the end, then follow the signs towards “Belval”. On the campus, there are no signs to indicate the way to Maison du Savoir. Please use the map below to find your way.
If you arrive by train, the stop is “Belval Université”. Our building is 10 minutes away from the train station by foot. There are also several buses that you can take to arrive on the campus.
For workshop 3 (focusing on number theory), if you wish to prepare the class before the workshop, you can review or introduce the following concepts:
a) The Euclidean division (i.e. the division with remainder) and the Euclidean algorithm (for the division, the case of a negative dividend/divisor should also be considered).
b) The Greatest common divisor (gcd) of two integers and Bézout’s identity that gives the gcd of two integers as a linear combination of these integers. (For example 3 = gcd(6, 15) = -12*6 + 5*15). Such a linear combination can be obtained by means of the extended Euclidean algorithm.
c) The definition of a prime number.
d) The basic rules of exponentiation.
Materials that can be used for the preparation will be provided.
At the end of a workshop, each student receives a certificate attesting to his participation.